
Department of Electrical & Computer Engineering
Signal and Image Laboratory (SaIL)
The University of Arizona®
|
|
|
|
Past Research |
Robust Watermarking of Digital Images
Student: Te-shen "Dickson" Liang
| |
With the advent of multimedia technology and the popularity of
Internet communications, there has been great interest in using
digital watermarks for the purpose of copy protection and
content authentication.
Digital watermarking technology allows the content
owner to embed a secret signature, i.e., watermark,
into the host content for many applications.
For digital watermarking, the major challenge lies in the
confident verification of the embedded watermark,
even after the watermarked content undergoes various forms
of unintentional or malicious modification.
Approaches aiming to guarantee reliable verification
of an imperceptible watermark are termed
robust watermarking algorithms.
Block diagrams of a typical watermark encoder and decoder, respectively:
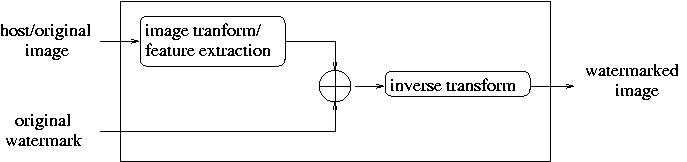
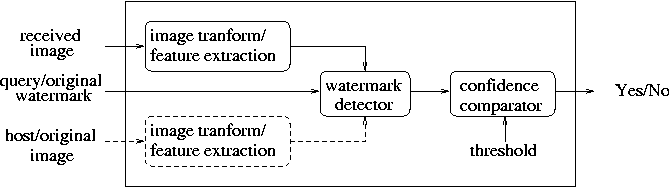
In this work, we developed more robust digital image watermarking
algorithms for reliable watermark verification,
assuming various types of non-malicious image processing.
Three new algorithms based on attack analysis, spectrum equalization,
and a modified embedding rule were developed.
We analyzed the proposed solutions, and compared them
against conventional algorithms.
Since the watermark robustness is to be tested under various forms of image
processing, the watermark encoder can utilize the knowledge of some
possible attacks for a more secure embedding.
Our first solution toward robust image watermarking is to select
the set of best watermarking coefficients through attack
analysis using the unwatermarked, original image.
For transform-domain algorithms, the discrete cosine
transform (DCT) or discrete wavelet transform (DWT) are normally
used for decomposing the host image before embedding the watermark.
Due to the low-pass characteristic of most images, the DCT/DWT coefficients
generally vary in amplitude throughout the image spectrum.
This low-pass nature is an advantage
for many transform coders, but it does not facilitate a reliable watermark
extraction for many watermarking algorithms.
Our second solution for robust watermarking is the use of
a simple, invertible permutation operator to equalize the
transform coefficients before watermarking.
Many transform-domain schemes utilize a directly-proportional rule
for embedding the watermark.
This approach results in diminishing performance as the watermark
capacity increases.
Our third solution provides a new embedding scheme that is inversely dependent
on the magnitude of the selected transform coefficients.
Publications:
-
Te-shen Liang and Jeffrey J. Rodriguez,
"A Modified Robust Embedding Scheme for Faithful Watermark
Extraction," in Proc. 2000 IEEE Intl. Conf. on Image
Processing, Vancouver, B.C., Canada, Sept. 10-13, 2000, vol. 1, pp.
419-422. [ PDF ]
-
Te-shen Liang and Jeffrey J. Rodriguez,
"Improved Watermark Robustness Via Spectrum Equalization," in
Proc. 2000 IEEE Intl. Conf. on Acoustics, Speech, and Signal
Processing, Istanbul, Turkey, June 5-9, 2000, vol. 4, pp. 1951-1954. [ PDF ]
-
Te-shen Liang and Jeffrey J. Rodriguez, "Robust Image
Watermarking Using Inversely Proportional Embedding," in
Proc. 4th IEEE Southwest Symp. on Image Analysis and
Interpretation, Austin, TX, April 2-4, 2000, pp. 182-186. [ PDF ]
-
Te-shen Liang and Jeffrey J. Rodriguez, "Robust Image
Watermarking Using Robust Coefficients," in Security and
Watermarking of Multimedia Contents II, Ping Wah Wong and Edward
J. Delp III, Eds. Proc. SPIE, vol. 3971, 2000.
Presented at the IS\&T/SPIE Intl. Symp.,
Electronic Imaging 2000: Science \& Technology, San Jose, CA,
Jan. 23-28, 2000, pp. 326-335. [ PDF ]
|
|
1230 E. Speedway Blvd., P.O. Box 210104, Tucson, AZ 85721-0104
|
©2014 All Rights Reserved. |
| Contact webmaster
|
|
|
|
|
