 |
|||
|
|

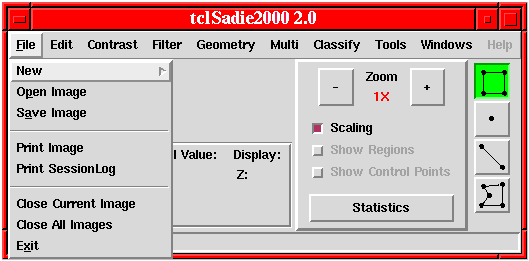
Click on the File > Menu Command above to see command information.
The File menu provides for creating new images with the New command and reading image data from disk in a wide variety of formats with the Open command. Image data may be written to disk with the Save Image command. The Print Image and Print Session Log commands print images or the contents of the session log window to a local printer or to a file for printing later. The current image or all images currently open may be disposed of using the Close Current Image or Close All Images command. To terminate a session and to exit from tclSADIE, select the Exit command.
The File > New menu provides for creating a variety of synthetic images based on user-provided parameters. This is very useful for creating image processing test patterns or functions for use in other tclSADIE routines, such as Filter > Convolution.
Click here for further details on File > New functions.
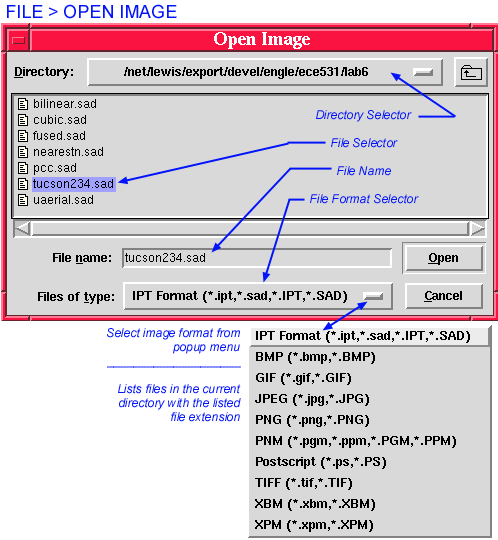
Select image type to open (FIles of type:) BEFORE selecting the file to open (File name:).
The File > Open command reads an image from disk and displays it on the desktop. tclSADIE can read images in its own native IPT (SADIE) format, as well as
formats. The dialog presented by the File > Open command is a standardized dialog used by many tcl/tk applications. At the top of its main window it displays the name of the current directory. The main window itself shows the contents of this directory, that is, all the files in the directory with the specified file extension, as well as any sub-directories. The hierarchy of directories may be traversed on available directory paths as with any other X-WIndows application. To select and open an image, either double-click on the file name, or select the file and click on the Open button.
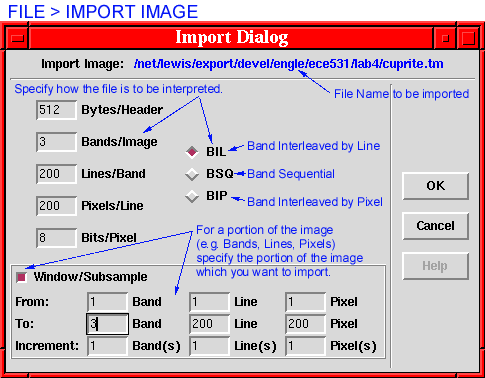
The File > Import command reads images created by applications other than tclSADIE,
or images transferred from other computers (“generic” images),
if they conform to one of the following three formats
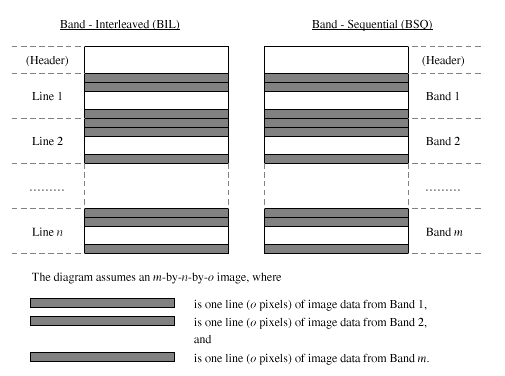
In addition to the controls from the Open command’s dialog, the dialog for the Import command requires specifying the parameters of the three formats above. The format itself is chosen with the BIL, BSQ, and BIP radio buttons, respectively. Other parameters, including: the size of the header (between 0 and 32K Bytes), the number of bands, lines/band, and pixels/line for image, and the number of bits/pixel (between 8 and 32) must be specified explicitly. The default header size is set for tclSADIE files at 512 bytes, the same as for IPT (MacSADIE) files. If the specified format does not exactly match the structure of the disk file, a variety of I/O-related error messages will result.
To load only part of an image, first specify the full image size as described above and then click on the Window/Subsample radio button. Then specify the bands, lines, and/or pixels to be windowed and/or subsampled. This area defaults to the entire image as specified in the primary dialog. This option is useful to view or process only part of the image, or if the entire image is too large to fit into available memory.
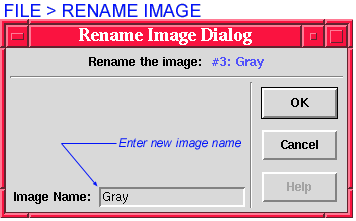
Entering a new Image Name changes the image name displayed in the title bar of the specified image. This command does not change the name of the file stored on disk.
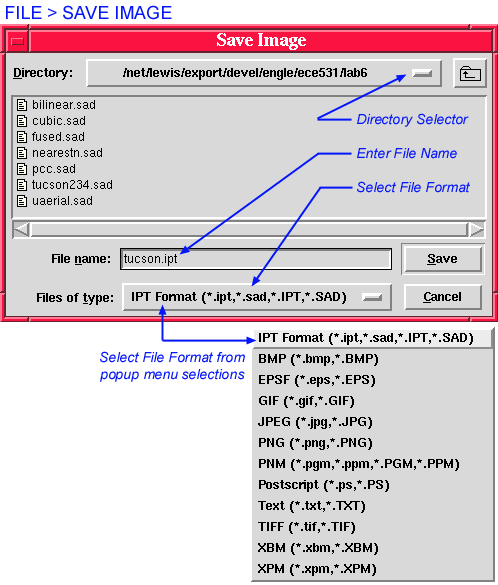
Select image type to save (FIles of type:) BEFORE entering the name of the file to save (File name:).
The File > Save Image command provides for writing an image to disk in tclSADIE’s IPT native file format, as well as
formats. The dialog presented by the File > Save Image command is a standardized dialog used by many tcl/tk applications. At the top of its main window it displays the name of the current directory. The main window itself shows the contents of this directory, that is, all the files in the directory, as well as any sub-directories. The hierarchy of directories may be traversed on available directory paths as with any other X-WIndows application.
To save an image, select the type in which to save (Files of type:) and enter a filename (File name:). Additional parameters may be specified for IPT, JPEG, and TIF file types. See below for descriptions of these options. If you do not understand what the additional options do, accept the default values.

With the number of bits/pixel packing set to 32, graylevel values are written to disk in full floating-point format. This is the default for IPT (SADIE) files. To reduce the disk space required to store an image, set the number of bits/pixel to any number n, 8 <= n <= 32. If the image graylevel values are in the range 0,2n–1, each pixel is then converted to an integer in the range 0,2n –1 (by having its fractional part truncated), and written to disk in n-bit integer format.

Quality:
Compression quality (0..100; 5-95 is useful range). Default value:
75. Higher number means higher quality and larger file.
Smooth:
Perform smoothing (10-30 is enough for most GIF's). Default value:
0 . Usually not necessary to perform any smoothing.
Grayscale:
Force image to grayscale and create a monochrome image file. Default
Value: Off.
Progressive:
Create progressive file (JPEG only). Allows for progressive levels
of resolution refinement while loading the image with a web browser.
Default Value: Off.
Optimize:
Optimize Huffman table. Default Value: Off.

User may control the level of compression (default is no compression, TIF files are normally used for exchanging images losslessly) and the byte order for different platforms. Default byte order selects the appropriate value for the current platform. Little(Small) Endian forces the byte order for PC/UNIX platforms. Big Endian (Network) forces the byte order for Macintosh platforms.

Images may be printed to a local printer or to a postscript file using the File > Print Image command.

The Session Log may be printed to a local printer or to a postscript
file using the File > Print Session Log command. Page X: indicates how far from the left edge of the paper to begin printing.
Page Y: indicates how far from the bottom of the page to begin printing.
Page measurement units may be specified as a number followed by
i - inches, c - centimeters, or m - millimeters.
Page anchor: indicates in which corner of the paper to anchor the document,
nw (northwest) would be the upper-left corner.
Closes the currently active image. The name of the currently active image is shown in the Main Screen under Current Image:. The current image is also indicated with a blue frame inside its window.
Closes all of the currently open images. Useful for cleaning up the desktop before going on to another task.
Returns a dialog box to confirm ending the tclSADIE session, click OK to end the current tclSADIE session.
Last Updated: August 2000
University of Arizona
Electrical and Computer Engineering Department
Digital Image Analysis Laboratory © 1999,2000